C5 petroleum resin is formed by polymerizing in the presence of a catalyst with C5 fraction, a by-product of the ethylene plant, as the main raw material. The resin is inexpensive and has excellent properties such as acid resistance, alkali resistance, aging resistance, and weather resistance, and is widely used in coatings, inks, seals, and adhesives.
Structure
The main chemical structural formula of C5 petroleum resin is shown in the figure:
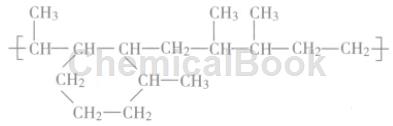
C5 petroleum resin is a thermoplastic resin with low relative molecular weight. Generally, the average molecular weight is between 1000 and 3000. The resin is yellow to light brown. Insolvents such as benzene, toluene and xylene, it is miscible with EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer) and polyethylene. Melting point, the softening point is usually determined by the Ring and Ball method. The softening point is the most important property of C5 petroleum resin, which marks the hardness, brittleness and viscosity of petroleum resin. At present, the C5 petroleum resin produced in China can be divided into two series according to the softening point: 80~110℃ and 110~160℃.
Classification
C5 petroleum resin is a by-product with a large output in the ethylene industry, and its effective utilization has become an important issue in rationally using petroleum resources and reducing the cost of ethylene production. According to different raw materials, C5 petroleum resins can be roughly divided into the following categories: mixed C5 petroleum resins, the raw materials can be mixed C5 fractions that have undergone preliminary separation or unseparated; aliphatic C5 petroleum resins, mainly concentrated piperylene Components; Dicyclopentadiene aliphatic C5 petroleum resin, with dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) as the main raw material; DCPD) copolymer resin with other substances; hydrogenation modified petroleum resin.
1. Mix C5 petroleum resin
C5 raw materials are directly mixed to generate C5 petroleum resin without separation, or C5 petroleum resin is synthesized through preliminary separated C5 raw materials, which is a commonly used method for synthesizing C5 petroleum resin. Its production process is generally first treated at high temperature to polymerize diolefins to form dimers, and after the dimers are separated, polymerization, neutralization, alkali washing, post-treatment, and solvent recovery are carried out, and finally, C5 petroleum resin is obtained. This method has the advantages of less investment, quick effect and simple process.
2. Aliphatic C5 petroleum resin
Aliphatic C5 petroleum resin, with concentrated piperylene as the main component. Light color, good heat and weather resistance, low softening point, compatible with non-polar polymers, incompatible with polar polymers, widely used as tackifier (pressure-sensitive adhesive, hot glue), rubber co-polymer Mixtures and used in the production of road marking paints.
3. Dicyclopentadiene aliphatic C5 petroleum resin
Dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) aliphatic C5 petroleum resin is obtained by thermal polymerization or cationic catalysis of high-purity dicyclopentadiene in the by-product of petroleum cracking to ethylene. The resin has a high degree of unsaturation, thermal reaction performance, and stable resin It has poor performance and is not used much directly, but it is an important raw material for chemical graft modification to prepare other high-grade resins.
4. C5/C9 copolymer resin
At present, the petroleum resins used in the rubber industry mainly include C5 and C9. Due to the difference in relative molecular mass and structure, C5 petroleum resin and C9 petroleum resin have different characteristics. C5 petroleum resin has the advantages of light color, good compatibility with natural rubber, heat resistance, oxidation resistance and light aging resistance, and storage stability, so it is widely used as a tackifier resin for natural rubber and synthetic rubber. But its softening point is lower and its relative price is higher. C9 petroleum resin has a darker color and is less compatible with natural rubber due to its high polarity, and can only be compatible with styrene-butadiene rubber. However, C9 petroleum resin has a wide range of raw materials, a relatively low price, and it is easy to obtain rubber resin with a high softening point. According to the introduction of relevant literature, the resin obtained by the copolymerization of C5 and C9 can integrate the advantages of C5 petroleum resin and C9 petroleum resin, has wide applicability and moderate price, and thus has a broad market prospect.
5. Hydrogenation modified C5 petroleum resin
Hydrogenation modification mainly includes three methods: slurry state, fixed bed and spraying. One-stage or two-stage hydrogenation process can be adopted. The process of hydrogenation is to mix resin and solvent, heat and pass hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. The hydrogen from the hydrogenation reactor can be passed into the reactor together with fresh hydrogen to achieve the purpose of recycling. The reaction product gas removes the solvent, and after cooling, it becomes the hydrogenated petroleum resin. Hydrogenated resins are mainly used for hot solvents, especially hot solvents that require transparency, which can increase adhesion and reduce costs. In foreign markets, petroleum resins are developing in the direction of high value-added products, and their added value mainly lies in their deodorizing effect and their heat resistance. The high-quality petroleum resins in the international market have a chroma of less than 3# and a softening point above 100°C. Hydrogenated petroleum resin technology is generally used. For example, in the coatings industry, C5 hydrogenated petroleum resins are used in the production of road marking paints to improve durability and weather resistance, extending their life from 1 year to 3 years. Another example is in the adhesive industry, the use of C5 hydrogenated petroleum resin to produce adhesives for disposable paper diapers and special sanitary napkins not only reduces production costs, but also significantly improves the chromaticity and mutual compatibility of the adhesives. properties and aging resistance.
Modified
Modified petroleum resin is not only the development direction of petroleum resin but also the foothold of many new materials. At present, there are two main types of chemical modification methods for petroleum resins. The first type is to add modifiers such as monoolefins, aromatic unsaturated hydrocarbons and alicyclic hydrocarbons to C5 raw materials, such as styrene modification. The second type is the graft copolymerization modification of petroleum resin with monomers with polar groups, such as maleic anhydride modification and styrene modification.
1. C5 petroleum resin introduces polar groups
Introducing polar groups into C5 petroleum resin can prepare petroleum resins with strong specificity and functional groups. , the introduction of polar groups can effectively solve this problem. Fu Jiansong used the C5 monoolefin fraction obtained from the C5 separation device to modify the piperylene petroleum resin. The effects of process parameters such as the addition method and amount of C5 monoolefin fraction, the polymerization temperature after addition, and the amount of catalyst and solvent on the properties of the product were studied. The results show that compared with the original resin, the modified piperylene resin has the advantages of narrower relative molecular mass distribution and lower melt viscosity on the basis of maintaining a higher softening point.
2. Hydrogenation modification of C5 petroleum resin
The purpose of hydrogenation of C5 petroleum resin is to saturate the double bond and part of the benzene ring in it, and to remove the residual halide of the C5 resin during the polymerization process, so as to improve its photothermal stability, reduce the chromaticity, and increase the softening point. Hydrogenation can also improve its compatibility with polyethylene, so that the adhesive strength and hue of the formulated adhesive are significantly improved.
3. C5 Petroleum Resin Emulsion
As people pay more and more attention to environmental protection issues and their own health issues, the use and discharge of organic solvents are restricted. Petroleum resin emulsion developed rapidly. The silicate product factory pulverizes the C5 petroleum resin to dissolve it in the solvent, and then adds the emulsifier aqueous dispersion and the emulsion stabilizer to make an emulsion, which is used in the production of exterior wall coatings, anti-rust coatings, waterproof coatings and adhesives etc., can also be used in foundry, paper and rubber industries. This emulsion uses C5 petroleum resin as the main raw material and water as the dispersion medium, which not only retains the characteristics of the original petroleum resin, but also has the characteristics of fast-drying, non-toxic, odorless, non-flammable, and safe to use. More importantly, it avoids the volatilization of organic solvents and pollution caused by discharge and meets the needs of green production and clean production.
Application
1. Tackifier
C5 petroleum resin is used in adhesives, involving the structure and decoration of the construction industry, automobile assembly, tires, wood processing, commodity packaging, bookbinding, hygiene products, shoemaking and other fields. C5 petroleum resin is a tackifying component of many adhesives, such as hot melt adhesives and pressure-sensitive adhesives.
2. Additives
As a paint additive, petroleum resin can speed up the drying speed of the paint film, improve water resistance, acid and alkali resistance, surface hardness and gloss, road marking paint containing 10%~30% hydrogenated petroleum resin has sufficient durability, good heat resistance. Stability and weatherability. Adding C5 petroleum resin (the dosage is about 15%) to the rubber can soften and increase the viscosity, which can improve the processing performance of the rubber. C5 petroleum resin is used. Petroleum resin can be used as the main additive of bituminous materials for house construction, sealing, coating and flood control construction, especially for laying colored pavement. In order to solve the problems of poor heat resistance, poor transparency and softness when using polypropylene or polybutene alone as medical containers and packaging materials (such as blood storage bags, liquid medicine packaging bags, infusion tubes, etc.), hydrogenated petroleum can be used. resin as an additive.
3. Petroleum resin for papermaking
Formulation of petroleum resins into emulsions can be used as sizing agents in the paper industry, thereby expanding the application areas of the finished resins. Since petroleum resin is a non-polar substance, it cannot be directly boiled into a sizing emulsion. It must be mixed with maleic anhydride and rosin with active groups. The development and application of petroleum resin for papermaking in my country started relatively late. The Institute of Chemistry has synthesized many kinds of petroleum resins for papermaking by thermal polymerization and has carried out a lot of experiments on their sizing properties.
Preparation
The polymerization process of C5 petroleum resin includes cold polymerization, thermal polymerization and two-step polymerization. The choice of the polymerization process is closely related to the raw materials.
1. Cold polymerization process
The cold polymerization process is also called the catalytic-polymerization process. Friedel-Crafts catalyst (such as BF3 and A1Cl3) is used to obtain piperylene resin after cationic polymerization, alkali washing to neutralize the catalyst, water washing, and purification to remove unreacted materials and oligomers. . The raw material for cold polymerization is the piperylene fraction separated from the C5 fraction of ethylene cracking. The mass fraction of piperylene is generally 65% to 75%. The softening temperature and relative molecular weight of the resin are adjusted by adding monoolefin or/and styrene. distribution and compatibility, etc. The mass fraction of each component in the piperylene fraction of a company: n-pentene is 0.018%, n-pentane is 0.014%, isoprene is 0.735%, 2-pentene is 0.620%, 2-methyl- 2-butene is 2.190%, trans-piperene is 44.542%, CPD is 0.450%, cis-piperene is 27.420%, cyclopentene is 17.491%, cyclopentane is 3.658%, and DCPD is 0.130 %.
The cold polymerization process is used to produce piperylene resin. The mass fraction of the raw material is 50%~75%, and the maximum allowable mass fraction of isoprene is 3.000%, so as to prevent excessive crosslinking of the piperylene resin, resulting in The solubility and compatibility of pentadiene resin becoming poor, and the relative molecular weight is not easy to control. CPD and DCPD have higher reactivity, therefore, w(CPD) and w(DCPD) in the raw material are required to be less than 2.000% to prevent the formation of gel during polymerization, and cause the instability of DCPD resin and viscosity when used as an adhesive. Sexual deterioration. The temperature of the cold polymerization process is generally controlled at 20~60°C to prevent gel formation and control the degree of polymerization. Polymerization is a strongly exothermic reaction, and the reaction temperature is generally controlled by controlling the rate of addition of raw materials or catalysts, forcing external circulation, and removing heat with a cooling medium. The catalyst in the cold polymerization process can be added directly, and it can also be added after complexing with organic compounds such as phenol, aliphatic carboxylic acid, ether, aldehyde and alkyl aluminum compound. It is easier to realize continuous and uniform addition than solid A1Cl3 and is more suitable for the continuous production process.
2. Thermal polymerization process
CPD and DCPD can be prepared from ethylene cracking C5 and/or ethylene cracking C9, and their reactivity is higher, and the catalytic polymerization is easy to form a gel. CPD and DCPD have good thermal polymerization properties. In the C5 or C9 fraction, w (CPD) and w(DCPD) higher than 35.000%, C5 petroleum resin can be produced by thermal polymerization. The thermal polymerization process does not require a catalyst, there is no catalyst removal problem, no wastewater, and the process is simple and economical; however, the reaction temperature and pressure are high, the reaction time is long, and the color of the product is darker, which is limited in some fields. Some documents propose to use a peroxide initiator to carry out free radical polymerization, and the initiator is cumene peroxide, benzoyl peroxide, etc., and the color of the prepared product is light and bright.
3. Two-step polymerization process
The C5 fraction produced by ethylene cracking can be used to directly produce C5 petroleum resin. Because the CPD mass fraction in the fraction is as high as about 20%, cold polymerization will form a gel. Therefore, the production of full-component C5 petroleum resin is generally carried out through two-step polymerization. In the first step, the C5 fraction is thermally polymerized to synthesize dimers, trimers and tetramers, and then the dimers, trimers and tetramers are catalytically polymerized. The catalytic-polymerization route in the two-step polymerization is basically the same as that of the cold polymerization to produce piperylene resin, but there are obvious differences in the process conditions.
